The Thermoforming Experts
From custom packaging, housings, panels, trays and more, RapidMade offers high-quality, personalized thermoforming and vacuum forming services. We leverage innovative technology, experienced engineers and unparalleled guidance to help you identify the right manufacturing solution to satisfy your project needs, every time.
Amplify your competitive advantage and enjoy faster turnaround times – at a fraction of the cost – without compromising quality. To delve deeper into the thermoforming process, visit our website here. We’re also happy to answer any questions you may have about the process. Simply contact us directly!
Thermoforming Materials
Favored for their versatility, thermoplastics are highly durable and possess a wide variety of mechanical, thermal, chemical and cosmetic properties. At Rapidmade, we have the flexibility to produce thermoformed parts in incremental window sizes as small as 5” x 5” to decrease excess material usage, as well as parts as large as 4’ x 8’ in size.
Explore all of our available materials below:
HIPS (Polystyrene)
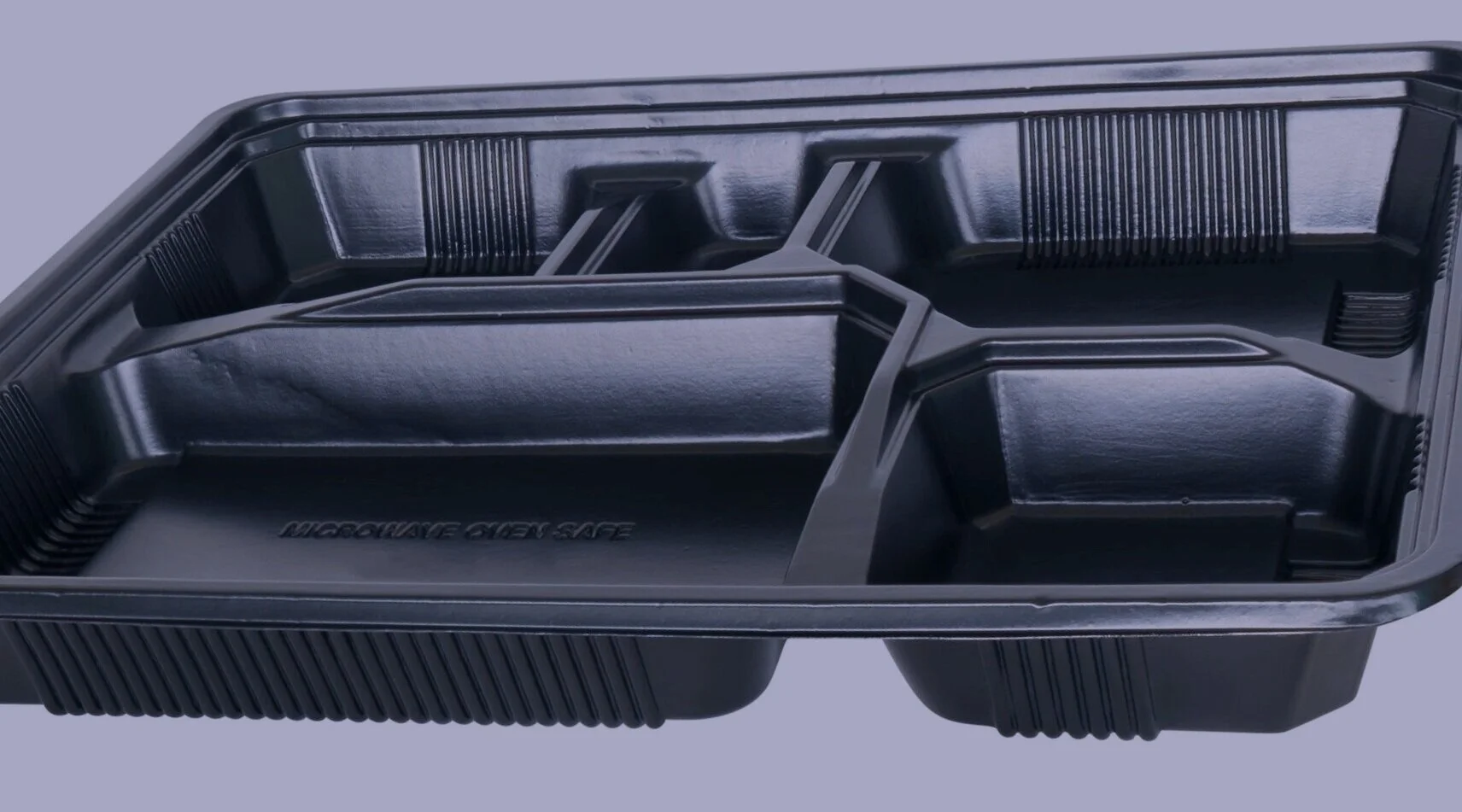
Our most commonly-used material. Inexpensive, functional thermoplastic, but can be brittle at low temperatures and off-gas at higher temperatures. Used for packaging trays, covers and light-duty structural pieces. Food-safe versions available.
PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate) (Polyester)
Moderately inexpensive material with good water and oxygen barriers. Able to stand up to substantially lower temperatures than HIPS. Often used for food-safe applications, freezer packaging and water bottles.
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene)
Medium-cost impact-resistant engineering plastic which can be flame retardant or UV resistant when blended with other materials. Used for high-end packaging and moderate-load structural components.
Kydex T (ABS/PVC) or Kydex 100 (Acrylic/PVC)
Expensive flame-retardant engineering plastic with high impact resistance. Used for moderate-load structures, covers and enclosures that require fire resistance. Kydex 100 is our go-to material for radomes.
PC (Polycarbonate)
Medium-cost engineering plastic with high stiffness, impact strength and temperature resistance, plus options for UV and scratch resistance. Often used for glass replacements on consumer electronics and high-temp applications. Harder to form than most thermoplastics, especially for fine details.
PE, HDPE or LDPE (Polyethylene)
Moderately hard, inexpensive plastic with high chemical resistance. Does not off-gas at high temperatures. Chemical and thermal durability makes it well-suited for chemical-resistant containers. Higher shrink rate than other materials, which lowers tool life and increases variability between parts.
PP (Polypropylene)
Moderately-priced alternative to PE which improves thermal and mechanical properties. Higher level of chemical resistance than most plastics. Can be used as an engineering plastic. Used for chemical-resistant applications, including food contact.
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride)
Hard engineering plastic with strong mechanical properties as well as high chemical and electrical resistance. Can be made rigid or flexible. Used for certain chemical-resistant containers.
Acrylic
An inexpensive, rigid and brittle plastic with relatively high UV resistance. More difficult to form than other plastics. Not intended for tight bends or details. UV resistance makes it well-suited to outdoor applications.



“Our company has procured industrial 3D printed parts through RapidMade for nearly 5 years now. We've been very happy with the service, quality, and price of parts using SLS and MJF processes; in addition, RapidMade sales engineers have been very helpful in recommending design tweaks to improve product outcomes.
“We've deployed these products in California, Colorado, Kenya, Rwanda and Ethiopia. Even now that we are no longer based in Portland, we still do our industrial 3D printing through RapidMade.”
— Taylor Sharpe, SweetSense Inc.